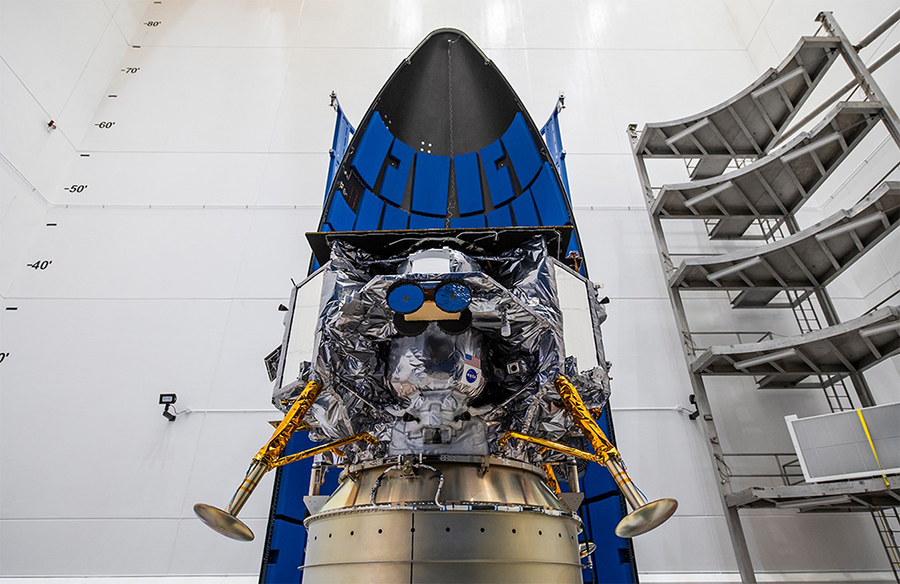
Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander continues to defy expectations, operating in orbit with growing optimism for an extended mission duration. Despite encountering challenges shortly after its launch aboard United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan Centaur, the spacecraft has surpassed expectations, demonstrating resilience and functionality in space.
Battling Adversity
Since its launch, Astrobotic has provided regular updates on Peregrine’s status, documenting the spacecraft’s journey on social media platform X. Following separation from the launch vehicle, engineers faced immediate complications, uncovering a critical fuel leak in Peregrine’s propellant system. Despite this setback, Peregrine has persevered, operating in space for over four days, surpassing initial estimates of operational time.
Extended Mission Duration
Initially, Peregrine was projected to have approximately 36 hours of propellant remaining. However, Astrobotic’s recent update indicates an extension to 52 hours as the leak’s impact gradually diminishes. This unexpected extension offers a glimmer of hope for an extended operational life in space.
Payload Success
Astrobotic has successfully retrieved critical data from numerous payloads onboard, including scientific instruments from NASA, the German Aerospace Center, and the European Space Agency. All payloads requiring communication with the lander have established contact, with power provided to ten active payloads. The remaining ten payloads are passive and do not rely on spacecraft communication or power.
Achieving Milestones
The operational success of onboard payloads marks a significant milestone, showcasing their capability to function effectively in space. Astrobotic acknowledges the dedication and resilience of the mission team amidst challenging circumstances, emphasizing the remarkable achievement under adverse conditions.
Looking Ahead
While the prospect of a soft moon landing remains unattainable, and the spacecraft’s lifespan is inevitably shortened due to the fuel leak, the extension of operational capabilities is a significant achievement. The Astrobotic team and payload contributors alike welcome this development, highlighting the potential for continued success despite initial setbacks.










Leave a Reply